As an Amazon Associate ,I earn from qualifying purchase .
Liver damage is a concern for many people due to the liver’s crucial role in detoxification, metabolism, and overall body health. Fortunately, natural strategies and lifestyle changes can help repair and regenerate the liver, supporting its essential functions. In this article, we’ll answer frequently asked questions about liver health, such as “How can I make my liver healthy again?” and “Can you fully repair your liver?” while offering insights into the best foods, vitamins, and lifestyle habits for liver repair.
Types of Liver Disease
Liver disease encompasses various conditions that damage the liver, affecting its ability to function. Understanding the common types can help in recognizing their unique symptoms and causes.
1. Fatty Liver Disease (Hepatic Steatosis)
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): This occurs due to fat accumulation in the liver not caused by alcohol. Risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol. NAFLD is common and can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves inflammation and potential scarring.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): Caused by excessive alcohol consumption, AFLD can lead to liver inflammation (alcoholic hepatitis) and eventually cirrhosis if drinking continues.
2. Cirrhosis
- Cirrhosis is advanced scarring of the liver due to chronic damage, often resulting from long-term hepatitis, excessive alcohol consumption, or other liver conditions. This irreversible scarring prevents the liver from functioning normally, posing severe health risks.
3. Hepatitis (A, B, C, D, and E)
- Hepatitis refers to liver inflammation, commonly caused by viral infections. Each type has unique transmission methods:
- Hepatitis A and E are often contracted through contaminated food or water.
- Hepatitis B, C, and D are typically transmitted through blood, bodily fluids, or shared needles.
4. Autoimmune Liver Diseases
- Conditions like autoimmune hepatitis occur when the immune system attacks liver cells. Other autoimmune conditions, such as primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis, target the bile ducts, leading to scarring and potential liver damage over time.
5. Liver Cancer
- Primary liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) arises in the liver cells, while metastatic liver cancer originates in other organs and spreads to the liver. Risk factors include chronic hepatitis infections, cirrhosis, and fatty liver disease.
Early Symptoms of Liver Disease
Liver disease symptoms often vary by condition and can be subtle in early stages. Here are the most common symptoms:
- Fatigue and Weakness
Chronic liver disease frequently causes fatigue and a general sense of weakness. These symptoms result from the liver’s inability to properly process toxins and support energy production. - Jaundice (Yellowing of Skin and Eyes)
Jaundice occurs due to a buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment, in the bloodstream when the liver is unable to process it effectively. This discoloration often starts in the whites of the eyes and skin. - Abdominal Pain and Swelling
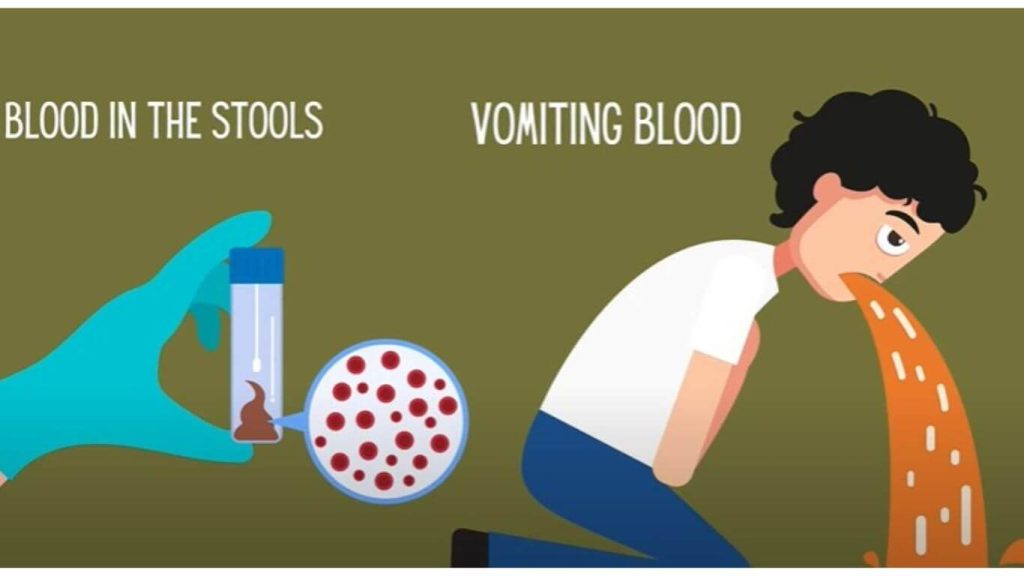
Pain or tenderness in the upper right abdomen, where the liver is located, can indicate liver inflammation or enlargement. Ascites, or abdominal swelling due to fluid accumulation, is also a sign of advanced liver disease. - Nausea and Vomiting
Digestive symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite are common as the liver’s reduced function affects metabolism and digestion. - Swollen Legs and Ankles (Edema)
Cirrhosis and other liver diseases can lead to fluid retention in the legs and ankles, causing noticeable swelling. - Dark Urine and Pale Stool
Dark-colored urine can occur due to increased bilirubin levels, while pale or clay-colored stool indicates a problem with bile flow from the liver. - Itchy Skin (Pruritus)
Chronic liver disease can cause itchy skin, often due to bile salt buildup in the skin. - Bruising Easily
A damaged liver struggles to produce clotting proteins, making bruising and bleeding more common.

Analytical Breakdown: Key Indicators and Risks of Liver Disease
Understanding the risk factors and signs of liver disease allows for earlier detection and intervention. Here’s an analysis of the major contributing factors and how they affect liver health.
1. Alcohol Consumption and Liver Damage
- The liver metabolizes alcohol, but excessive drinking over time leads to inflammation and scarring. Fatty liver disease can develop with even moderate drinking, especially in those with genetic predispositions.
- Statistical Insight: The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism reports that chronic alcohol consumption is responsible for 40-50% of liver disease cases in the U.S. annually.
2. Obesity and Diet
- Fatty liver disease is increasingly common in individuals with obesity and poor dietary habits. High intake of saturated fats and refined sugars contributes to fat buildup in the liver.
- Statistical Insight: According to recent studies, NAFLD affects about 25% of adults globally, and prevalence continues to rise alongside obesity rates.
3. Viral Hepatitis Infections
- Hepatitis B and C infections are among the leading causes of liver cancer due to chronic inflammation and scarring.
- Statistical Insight: The World Health Organization estimates that around 296 million people worldwide are living with chronic hepatitis B, and around 58 million have hepatitis C.
Advanced Symptoms of Liver Disease
As liver disease progresses, symptoms become more severe and indicate advanced liver damage. Recognizing these signs can prompt urgent medical attention:
- Mental Confusion (Hepatic Encephalopathy)
Toxins in the blood that the liver fails to process affect brain function, causing confusion, disorientation, and, in severe cases, coma. - Severe Jaundice
Advanced liver disease can cause intense jaundice, affecting the entire skin surface and eyes. - Rapid Muscle Wasting and Weakness
Muscle wasting can occur due to metabolic changes and nutrient absorption issues, often seen in advanced cirrhosis. - Spider Angiomas
Spider-like blood vessels under the skin, particularly on the face and chest, can appear due to liver disease.
Diagnosis of Liver Disease
Liver disease diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies.
- Blood Tests: Tests like the liver function panel measure enzymes (ALT, AST), bilirubin levels, and clotting factors, offering insights into liver function and potential inflammation.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRIs help visualize liver size, structure, and blood flow, detecting fatty liver, tumors, or scarring.
- Liver Biopsy: A biopsy can assess the degree of liver damage and diagnose specific conditions like cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Early detection through regular checkups is essential, especially for those with risk factors like a family history of liver disease, alcohol use, or obesity.
Preventing Liver Disease
Prevention is key in liver health. Following these guidelines can lower the risk of liver disease:
- Limit Alcohol Intake
Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption is one of the most effective ways to prevent liver disease. For men, moderation is considered up to two drinks per day; for women, it’s one drink per day. - Follow a Liver-Friendly Diet
A diet rich in antioxidants, lean proteins, and fiber helps reduce fat buildup and inflammation. Avoiding processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats is essential for liver health. - Stay Physically Active
Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces fat buildup in the liver. Studies show that even moderate exercise can improve liver health in people with NAFLD. - Practice Safe Practices
Hepatitis B and C infections can be prevented by avoiding unprotected sex, not sharing needles, and getting vaccinated against hepatitis B. Healthcare workers should always follow safety protocols to reduce exposure risks. - Avoid Overuse of Medications
Certain over-the-counter drugs, especially acetaminophen (Tylenol), can harm the liver if taken in high doses. It’s essential to follow dosing guidelines and consult a healthcare provider for long-term medication use.
Treatment Options for Liver Disease
Treatment depends on the type and stage of liver disease:
- Fatty Liver Disease: Lifestyle changes, including weight loss and a healthy diet, are often enough to reverse fatty liver disease. In advanced cases, medication may be prescribed.
- Hepatitis: Antiviral medications help manage hepatitis B and C, while hepatitis A and E often resolve on their own with rest and supportive care.
- Cirrhosis: Managing cirrhosis involves dietary changes, medication to reduce symptoms, and in severe cases, a liver transplant.
- Liver Cancer: Treatment options include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapies, depending on cancer stage and patient health.
Understanding Liver Damage and Its Causes
Liver damage can stem from multiple factors, including poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and viral infections such as hepatitis. While the liver is incredibly resilient and capable of regenerating damaged cells, prolonged exposure to harmful habits can lead to chronic liver disease, fatty liver, and cirrhosis, which require medical intervention. However, understanding liver-supporting methods can help prevent or slow down liver damage, promoting long-term health.
How Can I Make My Liver Healthy Again?
To restore liver health, implementing lifestyle changes that minimize liver stress is crucial. Key steps include:
- Reduce Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol is one of the primary causes of liver damage. Reducing or eliminating alcohol allows the liver to focus on healing and regeneration.
- Manage Weight: Obesity, especially abdominal fat, increases the risk of fatty liver disease. Regular exercise and a balanced diet help maintain a healthy weight, reducing strain on the liver.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration aids liver function by flushing out toxins, supporting efficient cellular processes.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Consuming nutrient-dense foods with low saturated fat and refined sugars can ease the burden on the liver and support its natural detox processes.

How Can I Clean My Liver in 7 Days?
Detoxifying the liver over a short period, like seven days, requires focus on nutrient-rich, liver-supportive foods. Here’s a daily plan to optimize liver function in one week:
Day-by-Day Liver Cleanse Guide
- Day 1: Start with a glass of warm water with lemon in the morning to stimulate liver enzymes and aid digestion.
- Day 2: Incorporate leafy greens like kale and spinach. High in chlorophyll, they help neutralize toxins.
- Day 3: Add beets and carrots to your meals. Both are rich in beta-carotene and antioxidants which stimulate and support overall liver function.
- Day 4: Include fatty fish like salmon or trout, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids, known for reducing liver inflammation.
- Day 5: Consume citrus fruits like oranges, which are high in vitamin C, aiding detoxification.
- Day 6: Drink green tea, which contains catechins that help support liver function and reduce fat.
- Day 7: Add garlic to your meals. Garlic contains allicin, a compound that activates liver enzymes, flushing out toxins.
Consuming these foods in conjunction with plenty of water, herbal teas, and a reduction in processed foods will help support liver detoxification over a week.
Can You Fully Repair Your Liver?
The liver is one of the few organs capable of regeneration, but the extent of repair depends on the damage’s severity. Mild to moderate liver damage, such as early-stage fatty liver or inflammation, can often be fully reversed with dietary changes, regular exercise, and lifestyle adjustments. However, advanced conditions like cirrhosis cause scar tissue that is generally irreversible but manageable with a healthy lifestyle to prevent further damage.

Which Fruit Helps Clean the Liver?
Several fruits are particularly beneficial for liver health. They include:
- Grapefruit: Contains naringenin, an antioxidant that helps protect the liver by reducing inflammation and preventing cellular damage.
- Berries: Blueberries, blackberries, and strawberries are rich in polyphenols, which protect the liver from oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Lemons and Limes: These citrus fruits aid detoxification by stimulating bile production and improving digestive health.
- Apples: Apples contain pectin, a fiber that binds to toxins in the digestive tract, making it easier for the liver to process and eliminate them.
Including these fruits daily can contribute significantly to a natural liver cleanse, promoting healthier liver function.
What is the Best Vitamin for Liver Repair?
Vitamins play a pivotal role in supporting liver health and repair. Key vitamins for liver regeneration include:
- Vitamin E: Known for its antioxidant properties, vitamin E has been shown to reduce inflammation in people with fatty liver disease.
- Vitamin C: This vitamin supports the liver by neutralizing free radicals and promoting detoxification.
- B Vitamins: B vitamins, especially B12 and folate, support liver enzyme function and the detoxification process.
Incorporating foods rich in these vitamins—like leafy greens, citrus fruits, nuts, and seeds—will provide necessary nutrients for liver repair and support.
What is Best for Liver Protection?
Protecting the liver from damage is essential for overall health. Besides maintaining a balanced diet, these additional tips can help:
- Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods are often high in saturated fats, sugars, and additives that stress the liver.
- Avoid Smoking: Chemicals in cigarette smoke place additional strain on the liver’s detoxification processes.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing fat buildup in the liver.
Which Food is Strong for Liver?
Certain foods are highly beneficial for liver strength and function:
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts contain sulfur compounds and glutathione, which enhance detoxification.
- Turmeric: Curcumin in turmeric aids in reducing liver inflammation and may even promote liver cell regeneration.
- Nuts and Seeds: Especially walnuts, which are high in glutathione and omega-3 fatty acids, both essential for liver health.
Regular consumption of these foods supports the liver’s resilience and its ability to repair damaged cells.
What Foods Reduce Liver Disease?
Dietary choices play a significant role in managing and preventing liver disease. Here are foods known for their liver-protective qualities:
- Green Tea: High in catechins, green tea helps to reduce fat in the liver and promotes overall liver health.
- Oatmeal: High in fiber, oatmeal helps to regulate blood sugar and reduce liver fat.
- Olive Oil: Monounsaturated fats in olive oil reduce inflammation and protect against fatty liver.
- Garlic: Known to activate liver enzymes that aid in flushing out toxins, garlic is an excellent choice for liver health.
Avoiding foods high in refined sugars, processed oils, and trans fats while incorporating these foods can greatly reduce the risk of liver disease progression.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Liver Repair
Making lifestyle adjustments can have a long-term positive impact on liver health:
- Stay Hydrated: Water is essential for flushing toxins from the liver and supporting the body’s detox processes.
- Avoid Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications like acetaminophen can be taxing on the liver if used excessively.
- Practice Mindful Eating: Eat meals that are low in sugar and salt, and opt for smaller portions to prevent liver overburden.
Conclusion
Repairing liver damage naturally is a journey that requires consistency, a balanced diet, and active lifestyle changes. From managing your weight and consuming liver-friendly foods to reducing alcohol and smoking, many strategies can help your liver heal. While the liver is resilient, it’s essential to maintain good habits and limit exposure to harmful substances. Embracing these practices not only supports liver regeneration but also leads to a healthier, more vibrant life overall.
Frequently Asked Questions Recap
- How can I make my liver healthy again? Through diet, hydration, and lifestyle changes.
- Can you fully repair your liver? Yes, for minor damage; advanced conditions require medical support.
- Which fruit helps clean the liver? Grapefruit, berries, citrus fruits, and apples.
- What is the best vitamin for liver repair? Vitamins E, C, and B-complex.
- Which foods reduce liver disease? Green tea, oatmeal, olive oil, garlic, and cruciferous vegetables.
Adopting these habits supports liver repair and protects against future damage, promoting overall health and longevity.