As an Amazon Associate ,I earn from qualifying purchase .
Fat is an essential component of the human body, playing a crucial role in energy storage, insulation, and protecting vital organs. However, excessive fat, particularly in specific areas like the lower belly, can lead to numerous health complications. Lower belly fat, also known as visceral fat, is not just a cosmetic concern but a significant health issue linked to various diseases. In this article, we will dive deep into the disadvantages of excessive fat in the body and analyze the best strategies for fat removal, focusing on the keyword “how to remove lower belly fat.”

The Science Behind Fat Accumulation
Before addressing the methods to remove lower belly fat, it’s important to understand how fat accumulates in the body. The human body stores fat in two primary forms:
- Subcutaneous fat: This fat lies just under the skin and accounts for the majority of fat in the body.
- Visceral fat: This is the fat stored around internal organs, particularly in the abdominal cavity. Visceral fat is the more dangerous of the two, as it is metabolically active and can contribute to serious health conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
Lower belly fat is often a combination of both subcutaneous and visceral fat, but it’s the visceral fat that poses the greatest health risks.

The Disadvantages of Excess Fat
Excessive fat in the body, especially visceral fat, can negatively impact health in various ways:
Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
Fat, particularly visceral fat, increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. It raises the level of “bad” LDL cholesterol and lowers “good” HDL cholesterol, contributing to the development of plaque in arteries, which can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular complications.
Impaired Metabolic Function
Excess fat can cause insulin resistance, a condition where cells in the body do not respond effectively to insulin, leading to higher blood sugar levels. This is a precursor to Type 2 diabetes. The more fat one carries, especially around the abdomen, the higher the risk of developing metabolic syndrome—a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and elevated blood sugar levels.
Inflammation
Visceral fat produces inflammatory chemicals known as cytokines, which can lead to chronic inflammation. This inflammation increases the risk of various diseases, including cancer, arthritis, and autoimmune disorders. Chronic inflammation also accelerates aging and contributes to muscle degradation.
Hormonal Imbalance
Excess fat, particularly around the belly, disrupts the balance of hormones like estrogen, insulin, and leptin, which regulate appetite, metabolism, and fat distribution. Hormonal imbalances can lead to more fat storage, creating a vicious cycle that makes it difficult to lose fat.
Reduced Physical Function
Excess weight puts a strain on muscles, bones, and joints, leading to reduced mobility, fatigue, and a higher risk of injury. Obesity is a leading cause of osteoarthritis, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.
Mental Health Impact
The psychological effects of carrying excess fat are often underestimated. People with higher body fat percentages are more likely to experience depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem due to societal pressures and body image issues.

How to Remove Lower Belly Fat: Effective Strategies
Now that we understand the risks associated with excessive fat, particularly in the lower belly, let’s explore the most effective strategies for fat removal. These methods target overall fat reduction while emphasizing the stubborn area of lower belly fat.
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is the cornerstone of fat reduction. To lose belly fat, it’s essential to consume fewer calories than you burn. However, calorie reduction must be done intelligently to ensure that you don’t lose muscle mass or compromise your metabolism. Here are some dietary strategies that can help:
- Reduce sugar and refined carbs: Processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbs like white bread and pasta spike insulin levels, promoting fat storage. Focus on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Increase protein intake: Protein is essential for muscle repair and metabolism. A higher protein diet can reduce cravings and improve satiety, which helps in managing calorie intake. Lean meats, fish, eggs, legumes, and dairy products are excellent sources of protein.
- Eat fiber-rich foods: Soluble fiber, in particular, can reduce belly fat by slowing digestion and making you feel fuller for longer. Foods like oats, flaxseeds, fruits, and vegetables are excellent sources of fiber.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water supports metabolism, helps in digestion, and can prevent overeating by promoting satiety.

Incorporate Cardiovascular Exercise
Cardiovascular exercises, also known as aerobic exercises, are essential for burning calories and reducing fat. Activities such as running, cycling, swimming, or brisk walking can help you burn fat, including visceral fat. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has been shown to be particularly effective for belly fat reduction as it alternates between short bursts of intense activity and periods of lower-intensity recovery.
Strength Training
Strength training is another critical component of fat reduction, particularly around the belly. Building lean muscle mass increases your resting metabolic rate, meaning you burn more calories even when you’re not exercising. Focus on full-body strength training exercises such as squats, lunges, push-ups, and deadlifts. Incorporating core exercises like planks and Russian twists can help strengthen the muscles in the abdominal area, though it’s important to note that spot reduction (losing fat from just one area) is not possible.
Reduce Stress
Chronic stress leads to elevated levels of cortisol, a hormone that can cause the body to store fat, particularly in the abdominal area. Managing stress through mindfulness practices, meditation, yoga, or simply engaging in relaxing activities can help lower cortisol levels and reduce fat accumulation.
Get Adequate Sleep
Poor sleep is associated with weight gain, particularly belly fat. Sleep deprivation can alter the hormones that control hunger, leading to increased appetite and cravings for high-calorie foods. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support your weight loss efforts.
Avoid Excess Alcohol
Alcohol, especially in large quantities, can contribute to belly fat. It’s high in calories and can interfere with the body’s ability to burn fat. Reducing alcohol intake or eliminating it altogether can aid in belly fat reduction.
Track Progress and Stay Consistent
Monitoring your progress helps keep you motivated. Use a journal to track your food intake, exercise, and any changes in your body measurements. Remember, fat loss takes time, and consistency is key. Focus on sustainable lifestyle changes rather than quick fixes.
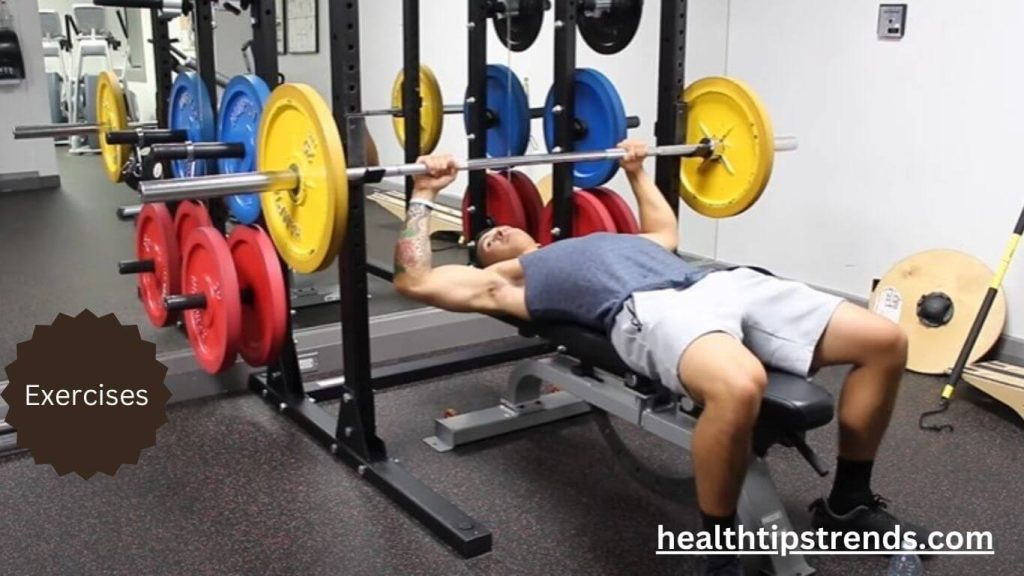

The Best Fat Removal Exercises
To effectively remove lower belly fat, you need a combination of cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and core-focused movements. These exercises help burn calories, increase metabolism, and build lean muscle mass, all of which contribute to fat reduction.
Cardiovascular Exercises: The Key to Burning Fat
Cardio exercises are essential for fat loss because they increase your heart rate, leading to more calories burned. Regular cardio helps reduce body fat, including visceral fat, which improves both your fitness and health.
- Running or Jogging: Running is one of the most effective exercises for burning calories and fat. A 30-minute run can burn up to 300-500 calories, depending on your intensity. It also engages the core muscles, which helps tone the abdominal area over time.
- Cycling: Cycling is a low-impact exercise that targets the legs and core while providing excellent cardiovascular benefits. Outdoor cycling or using a stationary bike can burn a significant amount of calories, helping with fat loss.
- Swimming: Swimming is a full-body workout that engages multiple muscle groups. It’s especially effective for people looking for a low-impact option to burn calories and improve cardiovascular health.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT involves alternating between short bursts of intense activity and brief periods of rest. It’s a time-efficient method that has been proven to target belly fat. A 20-minute HIIT workout, involving exercises like sprinting, jumping jacks, or burpees, can burn a significant number of calories while boosting metabolism.
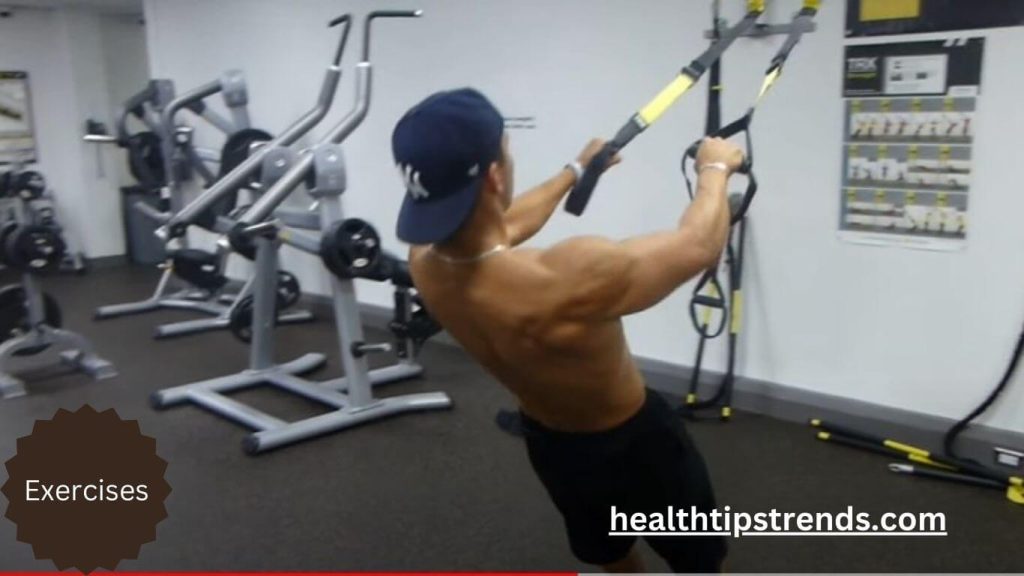
Strength Training: Building Muscle to Boost Fat Loss
Strength training is a critical component of fat loss because muscle burns more calories at rest than fat. By incorporating strength exercises, you increase your resting metabolic rate, which helps you burn more calories throughout the day.
- Deadlifts: This compound movement engages multiple muscle groups, including the core, back, legs, and glutes. It strengthens the lower back and abdominal muscles, helping to create a stronger core and reduce belly fat over time.
- Squats: Squats work the legs, glutes, and core muscles. This full-body movement increases calorie burn and improves muscle tone. Adding weights, such as dumbbells or a barbell, can make the exercise more challenging and effective for fat loss.
- Lunges: Lunges are excellent for toning the legs, glutes, and core muscles. Like squats, they increase calorie burn and improve lower body strength, contributing to overall fat loss.
- Planks: Planks are one of the most effective exercises for targeting the core. Holding a plank position engages the entire abdominal area, including the lower belly. Start by holding the plank for 30 seconds and gradually increase the duration as your core strength improves.

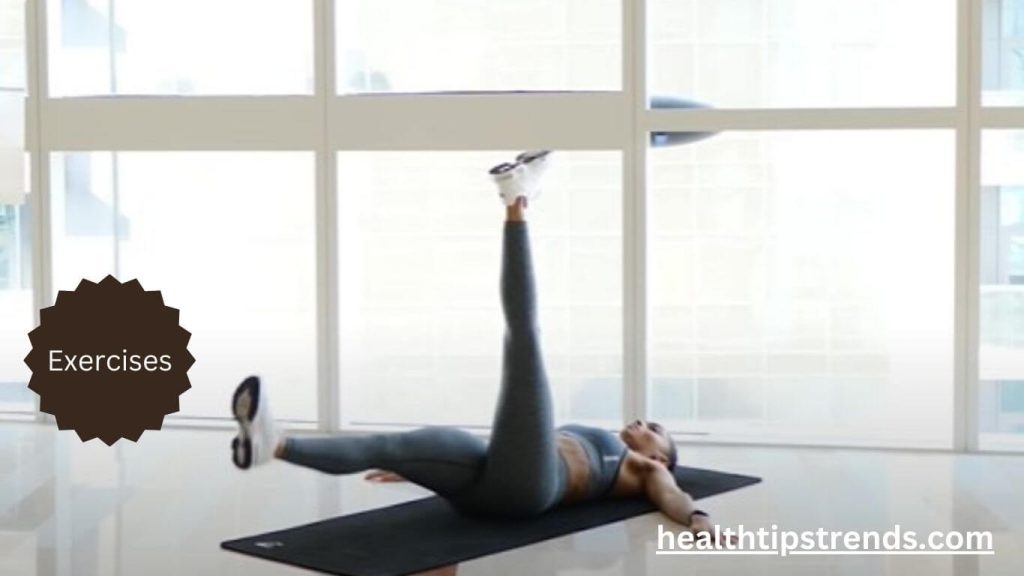
Core-Focused Exercises: Toning the Lower Belly
While cardio and strength training are essential for fat loss, core-focused exercises help tone the muscles in your abdominal area, giving you a firmer appearance as you shed fat.
- Leg Raises: This exercise specifically targets the lower abdominal muscles. Lie flat on your back with your hands by your sides, and raise your legs to a 90-degree angle. Slowly lower them back down without touching the ground, engaging your core throughout the movement.
- Bicycle Crunches: Bicycle crunches engage both the upper and lower abs. Lie flat on your back, lift your legs, and alternate bringing your elbow towards the opposite knee while twisting your torso. This movement strengthens the entire core, helping to tone the lower belly.
- Mountain Climbers: This full-body exercise engages the core, arms, and legs. In a plank position, bring one knee towards your chest, then switch legs quickly as if you’re climbing a mountain. This exercise elevates your heart rate, burns calories, and strengthens the core muscles.
Yoga and Pilates: Enhancing Flexibility and Core Strength
Yoga and Pilates are excellent for improving flexibility, posture, and core strength. These practices help tone the muscles and reduce stress, which is important for overall fat loss, including belly fat.
- Boat Pose (Navasana): This yoga pose strengthens the core, particularly the lower abdominal muscles. Sitting on the floor, lift your legs and lean back slightly, balancing on your sitting bones. Hold the pose as long as possible, engaging your core.
- Pilates Roll-Up: This exercise involves lying on your back and slowly rolling your body up into a seated position, engaging the core muscles throughout the movement. It helps strengthen and tone the abdominal muscles.
Common Myths About Lower Belly Fat Removal
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding belly fat removal. Let’s debunk some of the most common ones:
- Spot Reduction Is Possible: Many believe that doing exercises targeting the lower belly, such as crunches or sit-ups, will specifically burn fat in that area. However, fat loss happens uniformly across the body, and targeted exercises can only strengthen the muscles underneath the fat, not reduce the fat itself.
- Detox Teas and Supplements Work: Many products on the market claim to “melt away” belly fat, but there’s no scientific evidence to support these claims. Fat loss requires a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
- Starvation Diets Are Effective: Drastically reducing your calorie intake can lead to muscle loss and slow down your metabolism, making fat loss more difficult in the long run. Sustainable fat loss comes from a balanced approach to nutrition and exercise.
Conclusion
Excessive fat, particularly around the lower belly, presents serious health risks that extend beyond aesthetics. Cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorders, and inflammation are just a few of the dangers associated with excess visceral fat. However, with a combination of a balanced diet, regular cardiovascular and strength training, stress management, and adequate sleep, you can effectively reduce belly fat and improve your overall health.
By focusing on long-term, sustainable lifestyle changes and avoiding common myths and quick fixes, you can achieve your goals. Now that you understand “how to remove lower belly fat,” it’s time to implement these strategies for a healthier, happier you.






2 thoughts on “How to Remove Lower Belly Fat: Understanding the Disadvantages of Fat and Effective Strategies for a Healthier Body”